3 Volumes
Constitutional Era
American history between the Revolution and the approach of the Civil War, was dominated by the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. Background rumbling was from the French Revolution. The War of 1812 was merely an embarrassment.
History: Philadelphia and the Quaker Colonies
Philadelphia and the Quaker Colonies
Surviving Strands of Quakerism
Of the original thirteen, there were three Quaker colonies, all founded by William Penn: New Jersey first, Pennsylvania biggest, and Delaware so small Quakerism was overcome by indigenous Dutch and Swedes.
Quakers and Government

Unalienable Rights Before 1776

|
| Magna Carta |
In 1976, the bicentennial birthday celebration of the Declaration of Independence contained two major exhibits of its conceptual origins. Mr. H. Ross Perot of Texas loaned his copy of the 1215 Magna Carta, and the Proprietors of West Jersey loaned their 1677 original of William Penn's Concessions and Agreements to the colonists of New Jersey. The purpose of the exhibit was to emphasize the historical origins of the concepts within the Declaration, but even the language of the Concessions is remarkably similar, quite evidently lifted by Jefferson when he was writing. On one point, Penn had the better of Jefferson; he correctly wrote about inalienable rights, while somehow Jefferson gave us unalienable ones.

|
| William Penn |
The matter came up recently at a Socrates meeting of the Right Angle Club, where at least one member felt there was no such thing as a natural right, while others wavered. In discussing the rights which the Creator, William Penn and/or Thomas Jefferson may have given us, the various contexts must be held in mind. At the time of declaring our intention to sever relations with Britain's King, there was no Constitution to refer to as a source, and it was impolitic to assert the rights had been given by English kings, like King John. Therefore, the language cleverly short-cuts around the divine right of kings to make a direct connection between the Creator and the colonists. William Penn on the other hand, was a real estate promoter, offering enticements and assurances to prospective colonists who were naturally fearful of risking their lives in sailboats, only to face the possible tyranny of a vassal king who might be even worse than the anointed one. Not only did Penn renounce any suggestion of a Royal role for himself, but went to considerable length describing the legally binding concessions and agreements he was offering. The right of trial by jury, for example, became a right to be punished only by a jury of twelve of one's neighbors. He wasn't talking to lawyers, he was making important distinctions very clear to laymen. These were not rights given by a Divinity who could be trusted, nor something which grew out of Mother Nature. They were the personal promises of William Penn, in personal legal jeopardy of the English courts if he reneged on them. He even had a ready answer for those who discovered the religious language in legal documents -- the Quaker belief that, occasional appearances to the contrary notwithstanding, There is That of God, in every man.

|
| H. Ross Perot |
As a small sidelight of the Concessions document, it had long been housed in the little brick hut on Main Street in Burlington NJ, where the Proprietors of West Jersey keep their treasures. The obscurity of these papers was probably their best protection, but the risk of displaying them in Philadelphia at the centennial brought out the need to ensure them, hence to appraise their value. The figure of four million dollars was kicked around. Ross Perot might have felt comfortable with this sort of expense as the natural cost of being a rare book collector, but it seemed highly unnatural to Quakers. Sometime afterward, the Surveyor General, William Taylor, was awakened by a call from Burlington neighbors that someone was trying to break in the roof to steal contents of the Proprietorship building. The burglars were unaware that underneath the shingles, the roof was actually made of concrete a foot thick. So the perps were frustrated in their aims, but Bill Taylor was greatly troubled by the implications, actually unable to sleep at night worrying about what was in his custody. So, in time the State of New Jersey constructed a suitable archives building, and the valuable documents were transferred up to Trenton. Time will tell what the Soprano State does with such a valuable possession, but at least the Quakers can now sleep at night.
A Brief WILLIAM PENN CHRONOLOGY, 1644-1718
Born October 14,1644, in Tower Hill, London, England. Father Sir William Penn, Admiral who conquered Jamaica for King Charles II. Mother, Margret Jasper Vanderschuren, daughter of a Dutch merchant.
Education: Protestant Academy, Chigwell School, Oxford, Christ Church
Published a plan for "United States of Europe, EuropeanDyet, Parliment or Estates"
1666Joined Religious Society of Friends (Quakers)c.age 22 Outstanding swordsman. but frequent companion of George Fox.
1680 c. May. Petitions Charles II for a colony in America. June. Crown officials begin their consideration of WP's petition.
1681 January-February. Crown officials revise WP's draft of the charter for Pennsylvania.
4 March. Receives his charter for Pennsylvania.
14 March. Son William Penn, Jr. (1681-1720) is born.
April. Appoints William Markham as deputy-governor of Pennsylvania.
Writes Some Account of Pennsylvania, his first advertising pamphlet.
Spring-summer. Begins work on his constitution for Pennsylvania.
June. Begins lobbying to secure the lower counties (Delaware) from the Duke of York.
July. Announces his plan of land distribution in Pennsylvania.
July-August. Publishes a Map of Pennsylvania.
Takes his first land selling trip to Bristol.
August. His deputy governor arrives in Pennsylvania.
16 September. Writes to planters in Maryland, claiming the northern quarter of that colony.
September-October. Sees his first settlers and land commissioners off to Pennsylvania.
October. Writes a letter of friendship to the chiefs of the Delaware Indians.
1682 January-April. WP and Thomas Rudyard complete the first constitution and laws for Pennsylvania.
February-March. The Free Society of Traders founded.
c. 1 March. His mother, Lady Margaret Penn, dies.
25 April-5 May. Publishes his Frame of Government and Laws Agreed upon in England.
15 July. His agents conclude their first deed with the Delaware Indians.
24 August. Receives the deeds to the lower counties (Delaware) from the Duke of York.
30 August. Sails for America on the Welcome.
28 October. Lands at New Castle, Delaware.
October-November. Visits Chester, Pennsylvania, and the site of Philadelphia.
November. Visits New York and East New Jersey.
December. His first Assembly convenes at Chester.
Meets with Lord Baltimore concerning the Maryland-Pennsylvania boundary dispute.
Twenty-three ships arrive in 1681 -1682; the colony grows rapidly.
1683 January. Quakers begin meeting in Philadelphia; the Philadelphia County Court is established.
March. Visits East New Jersey and sits on its Council. Begins distributing large numbers of Philadelphia lots. His second Assembly approves a revised Frame of Government. 29 May. Meets with Lord Baltimore at New Castle. Spring-summer. Acquires his country manor Pennsbury, in Bucks County.
August. Writes Letter to the Free Society of Traders.
August-September. Tries to buy Susquehanna Valley lands from the Iroquois, but is blocked by New York's Governor Thomas Dongan.
September-November. Many ships arrive; both Philadelphia and Pennsylvania continue to expand.
October. Germantown surveyed.
November. Attempts to collect his quitrents.
1684 March. The Welsh Tract surveyed.
April-May. Decides to return to England to defend his boundary against Lord Baltimore.
May. Lord Baltimore leaves for England.
The Assembly passes an excise tax, which WP suspends.
July. Philadelphia's waterfront residents protest WP's city land distribution policy.
August. Prepares to leave for England; appoints Thomas Lloyd president of the Provincial Council.
18 August. Sails for England from Lewes, Delaware.
5 October. Lands at Worthing, Sussex.
October. Writes to Thomas Lloyd to get copies of documents needed for his defense against Lord Baltimore.
Meets with Charles II and the Duke of York.
December. The Lords of Trade postpone the hearing of the Penn-Baltimore controversy.
Died July 30, 1718, Ruscombe, UK.
William Penn, Justice Holmes, and the Inner Light

|
| William Penn |
WILLIAM Penn and Oliver Wendell Holmes, both lawyers, can be imagined debating fiercely across two centuries, about The Inner Light. Holmes famously stated his position at the opening of his book The Common Law : "The life of the law has not been logic, it has been experience." Penn, on the other hand, urged his Quaker followers to strip away centuries of books, teaching, and traditions, viewing in quiet contemplation their individual Light Within. Since the other central Quaker belief is that "there is that of God in every man", the implication is that it is open to everyone to know the right behavior by thinking hard enough about it. No books, preachers, ceremonies needed, and in fact, such tokens of society's experience can be badly misleading. Penn did not forcefully pursue how much of the outcome came directly from God and how much was then elaborated by logic; his point was the truth is most readily discovered by contemplation, uncluttered by the world's discussion.

|
| Oliver Wendell Holmes |
That Penn would have acknowledged some truth to Holmes' position can be surmised from the struggle he had with the argument that solitary contemplation cannot lead to an organized moral code of behavior within a society. The example of his time was the Hippie generation, is a more familiar example. What is to prevent a society which depends on silent introspection from concluding that monogamy,personal Hygiene,, and recreational drug avoidance are useless intrusions into the joy of personal freedom? Responses having to do with sexually transmitted disease, harm to the education and welfare of unparented children, disagreeable responses to the undesirable body odors of others, and the spread of addiction by example to those who wish to minimize unnecessary temptations, are all examples of hostility by others who may not have achieved equal illumination from their inner lights. Over centuries of observed experience, societies have reached comparatively similar views on what behavior should be prohibited by force, or discouraged by social pressure. Societies which reach these conclusions may hold themselves open to discussion, but often assert a right to punish those who violate the codes without offering plausible arguments beyond merely mystical ones, closed to debate.
Penn's response to such critiques was of the nature of insisting that Quakers obey the law unless the law insists on behavior prohibited by their religion. Within the realm of unwritten societal pressures, Penn was more relaxed. Sometimes he urged bizarre behavior having to do with hats and clothing, as a silent reproach to society on some issue, but in general, he urged that Quakers consider themselves Protestant Christians as a general guide to behavior. A century after he died, most Quakers were abandoning plain dress and plain speech as not plain at all, but ostentatious. Pointless and therefore ostentatious eccentricity could be harmful to the occasional truly important witness about such things as conscientious objection to war. If the considered purpose is to be taken seriously, eccentric behavior about trivial issues is to be avoided.
First Amendment: Separation of Church and State
 Amendment 1 Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press, or the right of the people peaceably to assemble and to petition the government for a redress of grievances. 
|
| The First Amendment |
Simplified histories of America often declare that other Western Hemisphere colonists mostly came to plunder and exploit; whereas English Protestant colonists came with families to settle, fleeing religious persecution. That's a considerable condensation of events covering three centuries, but it is true that before the Revolutionary War, eleven of the thirteen American colonies approximated the condition of having established religions. Massachusetts and Virginia, the earliest colonies, had by 1776 even reached the point of rebelliousness against their religious establishments. The three Quaker colonies (New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware) were late settlements, in existence less than a century before the Revolution, and still comfortable with the notion they were religious utopias. While differing in intensity all colonials respected the habits of thought and forms of speech, natural to utopians residing in a religious environment.
Once Martin Luther had let the Protestant genii out of its religious bottle, however, revisionist logic was pursued into its many corners. Ultimately, all Protestant questers found themselves confronting -- not religious dogmatism, but it's opposite -- the secularized eighteenth-century enlightenment. Comparatively few colonists were willing to acknowledge doubts openly about miracles and divinity. However, private doubts were sufficiently prevalent among colonial leaders to engender restlessness about the tyrannies and particularly the rigidities of the dominant religions. To this was added discomfort with self-serving political struggles observable among their preachers, and alarm about occasional wars and persecutions over arguably religious doctrines. Arriving quite late in this evolution of thought -- but not too late to experience a few bloody persecutions themselves -- the Quakers sought to purify their Utopia by eliminating preachers from their worship entirely. Thus, the most central and soon the most prosperous of the colonies made it respectable to criticize religious leaders in general for the many troubles it was believed they provoked.

|
| London Yearly Meeting |

|
| Congress Hall |
In all wars, diplomatic arts and religious restraints get set aside as insufficient, if not altogether failures for an episode of utter barbarism. In the Revolution, some Quakers split from pacifism and became Free Quakers, many more drifted into Episcopalianism, never to return to pacifism. The Constitutional Convention of 1787 was eventually held in this persisting environment; the previous service in the War counted for something, and the great goal was to strengthen the central government -- for more effective regional defense. A great many leaders were Masons, holding that much can be accomplished by secular leadership, independent of religious reasonings. Neither Washington nor Madison revealed much of their religious positions, although Washington the church attender always declined communion; Franklin and probably Jefferson were at heart deists, believing that God might well exist, but had wound up the universe like a clock to let it run by itself. The New England Calvinist doctrines have since evolved as Unitarianism, which outsiders would say theologically is not greatly different from deism. Physically surrounding the Philadelphia convention was a predominantly Quaker attitude; entirely too often, preachers get you into trouble.
When the first Congress finally met under their new constitution, they immediately confronted over a hundred Constitutional amendments, mostly submitted from the frontier and fomented by Jefferson and Patrick Henry, demanding a bill of rights. The demand within these amendments was overwhelming that the newly-strengthened central government must not intrude into the rights of citizens. Recognizing the power of local community action, states rights must similarly be strengthened. Just where these rights came from was often couched in divine terms for lack of better proof that they were innate, or natural. From a modern perspective, these rights in fact often originated in what theologians call Enthusiasm; the belief that if enough people want something passionately enough, it must have a divine source. The newly minted politicians in the first Congress recognized something had to be done about this uproar. Congress formed a committee to consider matters and appointed as chairman -- James Madison. Obviously, the chief architect of the Constitution would not be thrilled to see his product twisted out of shape by a hundred amendments, but on the other hand, a man from Piedmont Virginia would be careful to placate the likes of Patrick Henry. The ultimate result was the Bill of Rights, and Madison packed considerably more than ten rights into the package, in order to preserve the cadence of the Ten Commandments. The First Amendment, for example, is really six rights, skillfully shaped together to sound more or less like one idea with illustrative examples. Overall freedom of thought comfortably might include freedom of speech (and the press), along with freedom of religion and assembly, and the right to petition for grievances. But what it actually says is that Congress shall not establish a national religion. Since eleven states really had approximated a single established religion, the clear intent was to prohibit a single national religion while tolerating unifications within the various states. Subsequent Supreme Courts have extended the Constitution to apply to the states as well, responding to a growing recognition that religious states had the potential to get so heated as to war with each other. No matter what their doctrines, it seemed wise to deprive organized religions of political power as a firm step toward giving the Constitution itself dominant power over the processes of political selection.
At first however it was pretty clear; one state's brand of religion was not to boss around the religion of another state. Eventually within one state, Virginia for example, the upstate Presbyterian ministers were not to push around the Episcopalian bishops of the Tidewater. Madison and Jefferson saw well enough where political uprisings tended to start in those days, in gathered church meetinghouses. In this way, an Amendment originally promoted to protect religions had evolved into a way to ease them out of political power. The idea of separation of church and state has grown increasingly stronger, to the point where most Americans would agree it defines a viable republic. No doubt, the spectacle of preachers exhorting the same nation in opposite directions during the Civil War, settled what was left of the argument.
For Quakers, the most wrenching, disheartening revelation came when they were themselves in unchallenged local control during the French and Indian War. The purest of motives and the most earnest desire to do the right thing provided no guidance for those in charge of the government when the French and Indians were scalping western settlers and burning their cabins. Yes, the Scotch-Irish settlers of the frontier had unwisely sold liquor and gunpowder to the Indians, and yes, the Quakers of the Eastern part of the state had sought to buffer their own safety from frontier violence by selling more westerly land to combative Celtic immigrant tribes. A similar strategy had worked well enough with the earlier German settlers, but reproachful history was not likely to pacify frontier Scots in the midst of a massacre. The Quaker government was expected to do what all governments are expected to do, protect their people right or wrong. To trace the social contract back to William Penn's friend John Locke was too bland for a religion which prided itself on plain speech. Non-violent pacifism just could not be reconciled with the duties of a government to protect its citizens. The even more comfortably remote Quakers of the London Yearly Meeting then indulged themselves in the luxury of consistent logic; a letter was dispatched to the bewildered Quaker Colonials. They must withdraw from participation in a government which levied war taxes. And they obeyed.
Although the frontier Scots were surely relieved to have non-Quakers assume control of their military duty, the western part of the state has still neither forgotten nor forgiven. In their eyes, Quakers were not fit to be in charge of anything. Quaker wealth, sophistication and education were irrelevant; only Presbyterians are fit to rule. A strong inclination toward pre-destination lurks in that idea. Once more, the attractiveness of clear separation of church and state is reinforced.
The French and Indian War in fact had turned out fairly well; most of its victories were located on the European side of the Ocean, anyway. But twenty years later the Revolutionary War turned into a reassertion of the British conquest of all of North America, not merely the part to the west of the Appalachian mountains. To Americans, this came in the form of a demand for taxes to help pay off the costs of a war which greatly benefitted them. The Quaker colonies did not fully sympathize with rebellion, but they had once given up control of a territory larger than England rather than pay war taxes, so they were resistant to both sides in the dispute. Many prosperous and educated Quakers solved their dilemma by fleeing to Canada, but the ardent Quaker proposal for dealing with a coercive British government was not at all impractical. John Dickinson, in particular, argued that since the British motives were economic, success was most likely to come from economic counter-pressure, adroitly leveraged by three thousand miles of intervening ocean. That was shrewd and potentially effective. But the Scots-Presbyterian position was simpler and more direct. If you want us to fight your war, you are going to have to fight to win. The Virginia Cavaliers were probably more likely to win a conventional war if put in charge, but the blunt and almost savage frontiersmen were ideally suited for what has come to be called guerrilla warfare. Washington was a leader, French money was welcome and Ben Franklin was a diplomat, but the clarion call to this particular battle was the voice of Patrick Henry. All in all, the issue of established religion was far more complicated than merely the affirmation of a right to free exercise of religious belief. What united all the colonies was a recognition that, using the church, an arm of the government was just as likely to cause trouble as conducting the state as an instrument of church interests. Eventually, considering how religious America was at the time, there was remarkably little resistance to the firm separation of Church and State in its Constitution.
John Dickinson, Quaker Hamlet

|
| John Dickinson |
John Dickinson (1732-1808) would probably be better known if his abilities were less complex and numerous. It would have been particularly helpful if he had consistently remained on only one side of the important issues of his day. Born in a Quaker family and buried in a Quaker graveyard, he was for years a notable Episcopalian and soldier. He outwitted John Penn, the Pennsylvania Proprietor who was trying to keep Pennsylvania from sending representatives to the Continental Congress, by having the Pennsylvania representatives hold a meeting in the same small room of Carpenters Hall at the same time as the Congress. But he ultimately refused to sign the Declaration of Independence. Although he was the main author of the Articles of Confederation, the Constitution which replaced it would not have been ratified without his idea of a bicameral Congress. Although he was Governor of Pennsylvania, he was also Governor of Delaware, has been the central figure in the separation of the two states. In fact, for fifteen years he was a member of the Legislature of both states. Dickinson seems in retrospect to have been on every side of every argument, but he was immensely respected in his time.
Two events seem to have been central in the organization of his life. The first was his education as a lawyer. At that time and for a century afterward, lawyers were trained by apprenticeship. Dickinson, however, studied in London at the Inns of Court for four years and was by far the most distinguished lawyer in North America for the rest of his life. Furthermore, he absorbed the principles of the Magna Carta and the approaches of Francis Bacon so thoroughly that he never quite got over his pride in his English heritage. Throughout his leadership of the colonial rebellion, he acted as a better Englishman than the English themselves. His demand was for American representation in the British Parliament, not independence from England. It would not be hard to imagine Dickinson standing before a firing squad, gritting the words of St. Paul, Civis Romani Sum.
His other pivotal experience was the Battle of Brandywine. Dickinson had been the organizer or chairman of the two main Pennsylvania military organizations, the Pennsylvania Committee of Safety and Defense, and the so-called Associators (today's 111th Infantry, the first battalion of troops in Philadelphia). Both of these particular names were a characteristic gesture to conciliating pacifist Quaker feelings. Nevertheless, when Dickinson refused to sign the Declaration, he did temporarily become so unpopular he resigned his military commands. A few months later, when General Howe landed at Elkton at the narrow neck of the Delmarva peninsula, Dickinson enlisted as a common soldier to defend the southern perimeter of the defense line Washington had hastily thrown up to defend Philadelphia. Shortly afterward, Dickinson's friend and neighbor Caesar Rodney made him a Brigadier General in charge of the garrison around Elizabeth New Jersey, but the Battle of Brandywine taught an important lesson. Little states like Delaware and Maryland could not possibly defend themselves witho
A Pennsylvania Farmer in Delaware

|
| John Dickinson |
It is difficult to have a coherent view of the mind of John Dickinson. Seriously offended by the Townshend Acts, he rightly perceived them to be the work of a few malignant personalities in British high places who would mostly soon be replaced. Later on, he refused to be troubled by the inconsequential Tea Act, which he appraised as a face-saving gesture of reconciliation, but more recent historical information demonstrates was more likely aimed at avoiding an unrelated vote of no-confidence in Parliament. Unfortunately, Dickinson was too remote from these events and additionally could not comprehend reckless hotheads among his own neighbors. Reckless hotheads in turn seldom comprehend the measured meekness of Quakers. In any event, although Dickinson played a major role in the Declaration of Independence, he refused to sign it when the time came, evidently sensing an opportunity to separate the three lower counties from Pennsylvania and its Proprietors. A few months later when the British actually invaded the new State of Delaware on the way to capturing Philadelphia by way of Chesapeake Bay, Dickinson enlisted as a common soldier and fought at the Battle of Brandywine. Obviously, he was seriously conflicted.

|
| John Dickinson's Farmhouse |
Dickinson had become internationally famous for twelve letters he had meant to publish anonymously. The Letters From a Pennsylvania Farmer were written about 1768 out of resistance to the Townshend Acts. Because the three counties which were to become the State of Delaware were then still part of Pennsylvania, many school children have become understandably confused about the actual location of the man who became governor of both states, simultaneously.
The causes of the separation of the two colonies are still a little vague. Delaware schoolchildren are taught the two states separated, but often report they didn't retain much information about why it happened. The Dutch and Swedes who originally settled southern Delaware were not sympathetic with Quaker rule, which could be seen as a reaction to their living here for generations as Dutchmen before William Penn arrived, but then saw the colony sold out from under them. As a further conjecture, there might have been friction with the Quakers over slavery, similar to the hostility of other Dutch settlers in northern New Jersey when William Penn purchased that area. This pro-slavery attitude resurfaced in both areas during the Civil War. One alternative theory which has considerable currency in Delaware is local dissension about Quaker pacifism during the Revolutionary War. On a recent visit to Dickinson's home outside Dover, a school teacher was overheard to instruct his flock that the Dutch Delawarians wanted to fight the British King, but the Quakers wouldn't give them guns. "We value peace above our own safety," was the unsatisfying response they received from the Pennsylvania Assembly. But that line of reasoning bumps up against Dickinson's role in local affairs, his ambiguity over the Declaration, and his vacillation in warfare. One would suppose the simultaneous Governor of both states would play a major role in the separation of the two.

|
| over Air Force Base |
Dickinson's plantation, quite elaborately restored and displayed, is tucked behind the Dover Air Force Base. Perhaps all that aircraft noise will discourage sub-development in the area of Dickinson's plantation and the rural atmosphere may persist for years. At the time of the Cuban missile crisis, your correspondent happened to be driving past, observing the sky filled with bombers, just circling and circling until the diplomats settled matters. Since eight-engine bombers are seldom seen around Dover, it has always been my presumption that they came from elsewhere to be refueled at Dover; but that's just a presumption. One of the pilots later told me he was carrying nuclear "eggs" and was completely prepared to take a long trip to deliver them.
To get back to Dickinson's wavering about the Declaration, maybe there was a good reason to waver. Joseph J. Ellis (in His Excellency, George Washington) relates that after the devastating British defeat at the Battle of Saratoga, Lord North made an offer to settle the war on American terms. In a proposal patterned after the concepts of the separatists in Ireland, America could have its own parliament as long as it maintained trade relationships with England. As an opening offer, that comes pretty close to what the colonists had been demanding. Governor Morris was active in disdaining this offer, although it is unclear whether he was acting alone or as the agent of others. The offer came too late to be accepted, but it might have shortened the war by six years, and we might now have a picture of the Queen on our postage stamps.
REFERENCES
| His Excellency: George Washington: Joseph J. Ellis: ISBN-13: 978-1400032532 | Amazon |
| Letters From A Farmer In Pennsylvania To The Inhabitants Of The British Colonies (1903): John Dickinson: ISBN-13: 978-1163969533 | Amazon |
The Origin of States Rights, a Rumination
ALMOST alone among the British colonies in America, Pennsylvania's western border was specified in the King's charter of the colony. It was "five degrees longitude west of the point where the eastern boundary crosses the Delaware" [River]; however, its actual location on the ground was not actually marked until 1784. It's a few miles west of the present city of Pittsburgh, located at the forks of the Ohio River, where the Allegheny and Monongahela Rivers join. However, until 1784 it was not a certainty that this complex was within Pennsylvania instead of Virginia. The origin of Ohio is at the only major water gap in the North-South mountains, and the tributary rivers are fairly large. The three merging rivers thus form a nearly continuous water route along the base of the mountain range, from the Great Lakes south to Pittsburgh, or from the Chesapeake Bay north to Pittsburgh, and then to the Mississippi, going past the best topsoil farming land in the world. The forks of Ohio were the great prize of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth centuries, the place where young George Washington himself started the French and Indian War. To include these treasures, it seems vaguely possible that William Penn insisted on having the border of his state safely include the water gap at the beginning of Ohio. Perhaps not, of course, perhaps it was just a sense of tidiness on the part of the ministers of Charles II. The original document stated that the border was a hundred miles east of there, to match where Maryland ended. When the document was returned to Penn by the King's ministers, however, it had the new language.
The existence of this north-south termination of Pennsylvania began to take on a new significance when other states made claims for their land grant to extend to the Pacific Ocean, and the extensions collided with each other. Virginia then developed its territory to include modern Kentucky and West Virginia. That resulted in Virginia's land aspirations veering northward, to include the Ohio Territory west of Pennsylvania's fixed boundary. By the legal standards of the day, Virginia had a fairly good claim to all of the Indian territories, not merely to the west of Pennsylvania, but extending at least to the Great Lakes, perhaps farther. Maryland, Connecticut, New York, and Massachusetts had conflicting claims from an infinite extension of their western boundaries. As a consequence, it was impossible to achieve ratification of the Articles of Confederation for five years. The various states involved were fearful of the creation of a combined political entity might result in a court which would be enabled to rule against their individual aspirations. The stakes were high; the land mass involved would be several times as large as England.
The person who finally broke this deadlock might well have been Robert Morris, who was disturbed that this inter-state dissension was injuring his ability to borrow foreign funds for the Revolutionary War. The internal negotiations took place under wartime conditions, and are poorly researched. No doubt some person deserves credit for bringing this wrangle to a close. Virginia had the strongest claim, New York the weakest. New York gave up its claim first, Maryland was the last, and Virginia the most disappointed. Pennsylvania, unable to make a claim, took the position that the land belonged to everyone, and eventually was mollified by getting a small notch of land extending to the Great Lakes at Erie. It must be noticed in passing that final resolution of the land claims came at the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolution. Benjamin Franklin, soon to become President of Pennsylvania, was the negotiator of the treaty which reflected Pennsylvania's position that the land belonged to all of us, right?
Even without these western land claims, Virginia was the largest and richest of the colonies, and rather easily adopted the attitude that Virginia would be the leader of the new United States. From their viewpoint, the preservation of states rights would enhance Virginia's leading the country. More or less immediately, the attitude of small states like Delaware hardened into resistance that this must not happen. Much otherwise inexplicable behavior also begins to make a sort of sense: the perverse behavior of the Lee family in the Continental Congress, the quarrels within George Washington's cabinet, the relocation of the capital and the dreams of the Potomac as the nation's main portal of transportation, the rise of Jefferson's political party, the obstructionist behavior of Patrick Henry, the Virginia domination of the Presidency for decades, and countless less famous episodes of history -- make more sense as residuals of Virginia's early land aspirations, than as defenses of slavery or philosophical convictions that states were somehow superior to nations. These suspicions are difficult to clarify and impossible to prove. The best way to see some substance to them is to imagine yourself in the Virginia House of Burgesses, politically connected and vigorous, able to imagine your descendants all inheriting a county or two of rich land as a remote consequence of a few glamorous deeds by their Cavalier ancestor.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Being a Small Country

|
| very pleasant |
LIVING in a small country seems to be very pleasant, and many people prefer it to the hustle, bustle and high taxes of living in a large country. Unfortunately, big neighbors are tempted to conquer and enslave you. Aside from this one disadvantage, many people would prefer a simple, quiet life among blood relatives, all tending to think the same way. It's one step above tribalism, and maybe it's a form of peaceful tribalism.
|
| Measles |
But our evolutionary ancestors didn't think they could afford this luxury. They lived in a strange wilderness filled with fierce aborigines who often took a notion to scalp you, even if you were willing to become a hunter-gatherer like them, because they scalped other hunter-gatherers, too. And they were good at making war. Later historians sometimes contend that European settlers only gained a foothold in the New World because the Indians had been weakened by smallpox, measles, and other contagions which advanced ahead of the exploring Europeans. English settlers along the Atlantic coast were able to overcome the Dutch and Swedes who preceded them, but the French in Quebec and the Spanish in Florida were a greater threat. Worst of all enemies were the rulers of England, who seemed to think it was natural to enjoy the benefits of the New World without the nuisance of living there. A century or more of conflict from the enemies who surrounded them had pretty well convinced the English Atlantic settlers that they simply had to get bigger and stronger. Otherwise, one of the many enemies surrounding them would eventually succeed in what seemed to be a universal goal: conquest.

|
| The summer of 1787 |
The colonists had learned one other thing. Their own loose federation of small peaceful states was in some ways worse than rule by an outside King. The Confederation had been constantly reluctant to surrender local power to a unified defense; almost by definition, an invader was better disciplined than the defenders of a loose tribal alliance. The defense alliance had few advantages for keeping local bickering under control and was definitely less effective with families and children to protect against a mobile force of adult male warriors. The Confederation barely held together during an eight-year war against a common enemy, and it was rapidly coming apart after peace was declared in 1783. The English and French could see all this, too. Once they settled their own war with each other, each of them planned to envelop the former colonies. So George Washington and James Madison gathered the Best and the Brightest together in Philadelphia in the summer of 1787, intending to construct a practical plan for what almost all the colonists wanted: a Union. A Union strong and big enough so other nations would leave them alone. A Union was benign enough so its citizens would enjoy the same Liberty they had as a loose alliance. Divided informally into four interest groups, each of the four needed concessions to be made. But each also needed to leave the other three feelings they had gained something important as the price of surrendering to what some other group could not do without. Having found the vital concessions, it was then still necessary to tinker and re-balance, so that everyone could still "live with it". In essence: 1) The South had to be given time and forbearance to work out its difficult problem of slavery, moral qualms notwithstanding. 2) The nine small states had to be protected against perpetual domination by the three big ones, of Virginia, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts. 3) If America was to realize the full advantage of growing from thirteen states to fifty, existing old states must not take advantage of new ones. 4) Political revolution was not the end of it; there was also the Industrial Revolution. Fishing, lumbering, farming, trade, and cotton, would in some way need to accommodate banking and manufacturing, assisting rather than upsetting other compromises. Given these tangled issues, it would be a long, hot summer in Philadelphia.

|
| Treaty of Westphalia in 1648 |
Three of the four main problems were obvious, demanding to be addressed. Slavery was obvious from the start; you either solved this problem or the South would walk out. The western wilderness was bigger than existing America; it too could not be ignored. And finally, huge variations of climate and resources led to local specialization; a marvelous thing, if you could trust your suppliers and customers to cooperate. But curiously, none of these issues got directly to the political problem the Constitutional Convention was meant to solve, which was unifying thirteen different sovereignties, each of which was prepared to get up and walk out. The modern nation state was created by the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648; its guiding principle was mutual respect for local sovereignty. Having pacified over a hundred contentious central European states, it required a great deal of self-assurance for anyone to flout it. It seemed hard to imagine any way to remain sovereign, without commanding a vote equal to that of other sovereignties. The delegates from the State of Delaware, which had separated from Pennsylvania within the past decade, were "prohibited [by their legislature] from changing the Article in Confederation establishing an equality of votes among the States". Just what agitated the minds of the Legislature of Rhode Island was kept private, but something about a Union bothered them so much they refused to send delegates to Philadelphia even to discuss Union. After they assembled and started having dinner together at taverns, and later as they were beginning to vote in coalitions, one thing began to emerge. The small states banded together, hung out together, talked alike, and began to vote alike. Their emerging leader was John Dickinson of Delaware, the author of the Articles of Confederation, and very likely one of the prime agitators in the lower three counties of Pennsylvania -- breaking off from Pennsylvania and becoming the State of Delaware. Furthermore, Dickinson had been Governor of both Delaware and Pennsylvania, so he was very familiar with the deplorable behavior of the Legislature of Pennsylvania, now and for decades in the past. It took a long time for this sly old political operator to show his cards, but when he did, he gave James Madison the shock of his life. Madison, the near neighbor of George Washington and leader of the Virginia delegation, the author of the Virginia Plan, and the clear authority on the politics of government in America was busily consumed with working out the details of the emerging Constitution. Obviously, it went to his head a little, and so he was dumbfounded when Dickinson drew him aside in the corridor to tell him he wasn't going to have a Constitution at all. Dickinson was walking around with the votes in his pocket of five or six of the nine small states and was telling Madison that the small states were fed up, and not going along. Young Madison was suddenly confronted by the most respected lawyer in America, whose timing was perfect. For what may have been the first time in his life, Dickinson fully revealed the depth of his annoyance, that the big states would always take the little ones for granted. That the little ones were always expected to be deferential to the big fellows in charge of the big states. And then the clincher: "I would rather risk conquest from a foreign state than being forever dominated by my larger neighbors." That put it in a nutshell. If the only reason for joining a Union was to be protected from foreigners, Dickinson wasn't so sure he preferred his coalition partners. Evidently, this was the feeling of most of the other small states at the Convention, and it may well be the feeling of all small states, anywhere and everywhere.

|
| Promoting the Abolition of Slavery |
Once the Convention got the idea, solving it became comparatively easy, but why waste an opportunity? There is a good reason to suppose it was Ben Franklin, silent as a cat watching a mouse, who matched it up with slavery. His fellow Pennsylvania delegate, James Wilson, had prepared the way by starting the discussion of granting 3/5 representation for slaves, but it had received comparatively little notice in the previous few weeks. Franklin rammed it home, adding a sop to the large states by according to the House of Representative sole power to introduce money legislation. Two of the main issues of the convention were solved with one agreement, small-state representation, and slavery. Who can say how long he had been nursing this idea. He had agreed to be president of the Pennsylvania Society for Promoting the Abolition of Slavery, about a month before the Constitutional Convention began. Prior to that, he and his wife had owned a slave or two, for many years. On June 2, the society adopted a resolution to end the slave trade and presented it to Dr. Franklin, asking him to present it to the Convention. He never did, explaining later it was "advisable" to let the matter lie over. In August, Alexander Hamilton blocked a similar resolution from the New York Manumission Society, even though he had been a fervent lifelong opponent of slavery.
The Proprietorships of William Penn
William Penn became first interested in the Colonies when he acquired New Jersey as an investor in what started out as the bankruptcy proceedings of a client. Unlike his spoiled children and grandchildren, he was sincerely interested in helping the persecuted members of his new religion, and those who later totaled up his lifetime finances found that overall he lost money on his real estate ventures. His descendants, however, were mainly concerned with selling real estate, and soon reverted to Anglican church membership. When William Penn later received Pennsylvania and Delaware from the King of England (Charles II, the Stuart King restored with the help of his Admiral father), he not only owned these territories but for practical administrative reasons was offered the right to rule them. By then Penn's main future intention was to found a refuge for Quakers and other religious dissenters, so becoming a vassal King was graciously declined. Instead, he became a real estate Proprietor, after satisfying himself about the government and other arrangements in only a general way. At least half the original 13 colonies were also proprietorships, although the terms of their grants had great variation. Penn's intention for the proprietorship was to sell off as much of the property as possible, sort of benignly watching the process unfold in the parts he had sold.
There were two unforeseen flaws in this benevolent idea; the first was that his sons and heirs would abandon the Quaker faith and have little interest in his holy experiment except for the revenue it returned. The second flaw was to fail to see that vigorous religious toleration might eventually lead to the Quakers becoming outnumbered in their own refuge. Eventually, there does come a time in the real estate sell-off process when you have sold more than you retain. After that point, you may no longer dominate the politics, and in fact, that happened far sooner than half-way, because of Penn's unwillingness to employ force .

|
| William Penn |
In land value, although perhaps not in land area, that point of loss of control had been reached by the middle of the eighteenth century, and it led to a famous battle between the Penn descendants and Benjamin Franklin. The Penn family saw no justice in paying taxes on the land they hadn't yet sold, or obeying laws created by their customers which extended beyond the land they owned; if they wanted to rule it all, they should buy it all. Franklin took the part of the settlers and immigrants, who resented paying taxes and fighting Indians on behalf of someone who still owned vast stretches of the land "within" the colony. A significant factor in this peculiar argument is that Thomas Penn, the dominant chief of the family descendants, had a deep and abiding suspicion of Franklin, dating back to that episode related in Franklin's Autobiography where Franklin raised a militia in King George's War when the pacifist Quakers refused to do so. Both sides had some justice in their positions, both sides appealed to the King. The Penns knew the King better, so Franklin lost. That was mostly what Franklin was doing in London in the years before the Revolution, and eventually, it took a Revolutionary war to resolve the issue. Some have said the episode showed Franklin was not as shrewd a politician as history books would portray him. In fact, it more likely emphasizes that Franklin was a loyal British subject right up to 1775. His position was that all parties were and forever would be, inhabitants of the British Empire, so they had equality under British rule. The Penns felt they had a right to consider Pennsylvania their own sovereign property, under which the colonists had no rights until they paid for them. It is easy to see how the notion of independence could take hold in this curious reversal of roles. Nevertheless, Pennsylvania did resolve the issue with the appearance of lawfulness, although with restrained generosity. To quote Sydney G. Fisher, writing in The Quaker Colonies, "When the people could have confiscated everything in Pennsylvania belonging to the proprietary family, they not only left them in possession of a large part of their land but paid them handsomely for the part that was taken." The matter is generally considered to have been finally settled by the Confirming Act of 1787, although few would now contend that fifteen pennies per acre is or was a handsome price.
And so, the Pennsylvania proprietorship was dissolved. In New Jersey, on the other hand, the proprietorship still exists. The land between the North River (Hudson) and the South River (Delaware) was divided into two proprietorships by a line drawn between the Delaware Water Gap, and Beach Haven on Long Beach Island. The southern segment was called the Proprietorship of West Jersey, informally peopled by English Quakers, and a northern half, the Proprietorship of East Jersey, informally ceded to Scots Quakers who proved to be more Scottish than Quaker. Temperamental differences might well have eventually led the two segments to take opposite sides of the 1860 Civil War except that it was the northern half that sympathized with slavery and the Southern Confederacy, while the Proprietorship of West Jersey was mostly where the anti-slavery movement began, with a Quaker named John Woolman. As matters turned out, neither slavery nor taxing unsold land became irreconcilable issues in the Jerseys. Unsold land of the Proprietorship was already fairly minor in New Jersey at the time of the Revolution, but the issue hadn't been forgotten by the Proprietors, either. A couple of the stockholders of the proprietorship were members of the Constitutional Convention. When the time came that other delegates urgently needed New Jersey's vote to ratify the new constitution, the Proprietor problem was "explained" to the other states. The outcome was that the proprietorship tacitly agreed to be taxed and regulated like any other property owner, while their own rights were respected as persisting under the new Constitution. Such a sensible outcome was probably not possible in Pennsylvania because there was so much more unsold land to fight about. The peacefully accepted consequence in New Jersey, even today, is that when the ocean creates a new strip of beach or a farmer abandons some land on the other side of a turnpike, it reverts to the Proprietorship as undeeded and untitled land. As such, it legally belongs to a little group of stockholders who meet once a year in Burlington or Salem, under a tree, and who can actually pay themselves annual dividends. It is however only true in half the state; the Proprietorship of East Jersey surrendered its rights to the State in 1998.
In Delaware, things are a little fuzzier. Delaware was once part of Pennsylvania, as its lower three counties. John Dickinson was once Governor of both states, but they had two legislatures from 1700 to 1776. The last time the proprietorship matter came up, so far as real estate lawyers can remember, was in the shifting sandy beaches of Cape Henlopen; things were smoothed out by making the disputed land into a state park.
REFERENCES
| Encyclopedia of New Jersey | Google Books |
| The Problem of West Jersey | JSTOR |
| The Oxford History of the British Empire: The Origins of the Empire | Google Books |
| A Map of East and West New Jarsey | JPG |
| Council of Proprietors of West Jersey | westjersey.org |
| Magna Charta: Part I: The Romance of the Great Charter; Part II: Pedigrees of the Barons: John S. Wurts: SIN: AB0006D91C4 | Abe Books |
| West New Jersey: The Peculiar Province: ASIN: B00072HGTE | Amazon |
| Why the Private School?: Allan V. Heely: ASIN: B000GR1QS2 | Amazon |
Jury Nullification
 |
| Tom Monteverde |
We must be grateful to the late distinguished litigator, Tom Monteverde, for reminding us of the importance of the jury in American history. Juries seldom realize how much power they can have if they unite on a common purpose. In fact, juries have the implicit right to veto almost anything the rest of government does, by rendering it unenforceable. If the jury opinion is a majority view, nothing but a civil war can legally stop them. So it helped Washington to have jury nullification seem an invincible Quaker idea, while the South trusted a rich slave-owner who had renounced power.
 |
| William Penn |
The right to a jury trial originated in the Magna Carta in 1215, but a jury's essentially unlimited power was established four centuries later by Quakers. The legal revolution grew out of the 1670 Hay-market case, where the defendant was William Penn, himself. Penn was accused of the awesome crime of preaching Quakerism to an unlawful assembly, and while he freely admitted his guilt he challenged the righteousness of such a law. The jury refused to convict him. The judge thus faced a defendant who said he was guilty and a jury who said he wasn't. So, the exasperated judge responded -- by putting the jury in jail without food.
The juror Edward Bushell appealed to the Court of Common Pleas, where the problem took on a new dimension. The Justices certainly didn't want juries flouting the law, but nevertheless couldn't condone a jury being punished for its verdict. Chief Justice Vaughn decided that intimidating a jury was worse than extending its powers, so the verdict of Not Guilty was upheld, and Penn was set free. Essentially, Vaughn agreed that any jury that wasn't allowed to acquit was not really a jury. In this way, the legal principle of Jury Nullification of a Law was created. A verdict of not guilty couldn't make William Penn innocent, because he pleaded guilty. A verdict of not guilty, under these circumstances, meant the law had been rejected. Jury nullification thus got to be part of English Common Law, hence ultimately part of the American judicial system.
 |
| Andrew Hamilton |
This piece of common law was a pointed restatement of just who was entitled to make laws in a nation, whether or not nominally it was ruled by a king or a congress. Repeated British evasion of the principles of jury trial became an important reason the American colonists eventually went to war for independence, and probably a better one than some others. The 1735 trial of Peter Zenger was an instance where Andrew Hamilton, the original "Philadelphia Lawyer", convinced a jury that British law, blocking newspapers from criticizing public officials for improper conduct, was too outrageous to deserve enforcement in their court. In that case, jury defiance became even more likely when the judge instructed the annoyed jury that "the truth is no defense". Benjamin Franklin's Pennsylvania Gazette was here quick to come to the side of jury nullification, saying, "If it is not the law, it ought to be law, and will always be law wherever justice prevails." Franklin quickly became allied with Andrew Hamilton, who became Speaker of the Pennsylvania Assembly.
 |
| John Hancock |
The Zenger case was often stated to be the origin of the Freedom of the Press in our Constitution fifty years later, but in fact the First Amendment merely provides that Congress shall pass no laws like that. Hamilton had persuaded the Zenger jury they already had the power to stop enforcement of such tyranny, and the First Amendment could be seen as trying to prevent enactment of laws that will foreseeably incite a jury to revolt.
The Navigation Acts of the British government, for example, were predictably offensive to the American colonists, whose randomly chosen representatives on juries were then rendered useless with their wide-spread refusal to convict. This, in turn, provoked the British ministry. John Adams made a particularly famous defense of John Hancock who was being punished with confiscation of his ship and a fine of triple the cargo's value. Adams was later singled out as the only named American rebel the British refused to exempt from hanging if they caught him. As everyone knows, Hancock was the first to step up and sign the Declaration of Independence, because by 1776 there was widespread colonial outrage over the British strategy of transferring cases to the (non-jury) Admiralty Court. Many colonists who privately regarded Hancock as a smuggler were roused to rebellion by the British government thus denying a defendant his right to a jury trial, especially by a jury almost certain not to convict him. To taxation without representation was added the obscenity of enforcement without due process. John Jay, the first Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the newly created United States, ruled in 1794 that "The Jury has the right to determine the law as well as the facts." And Thomas Jefferson built a whole political party on the right of common people to overturn their government, somewhat softening, it is true, when he grasped where the French Revolution was heading. Jury Nullification then lay fairly dormant for fifty years. But since the founding of the Republic and the reputation of many of the most prominent founders was based on it, there was scarcely need for any emphasis.
 |
| Slave |
And then, the Fugitive Slave Law of 1850 began to sink in. It became evident that juries in the Northern states would routinely refuse to convict anyone under that law, or under the Dred Scott decision, or any other similar mandate of any branch of government. In effect, Northern juries threw down the gauntlet that if you wanted to preserve the right of trial by jury, you had better stop prosecuting those who flouted the Fugitive Slave law. In even broader terms, if you want to preserve a national government, you had better be cautious about strong-arming any impassioned local consensus. A rough translation of that in detail was that no filibuster, no log-rolling, no compromises, no oratory, no threats or other maneuvers in Congress were going to compel Northern juries to enforce slavery within their boundaries of control. All statutes lose some of their majesties when the congressional voting process is intensely examined, and public scrutiny of this law's passage had been particularly searching. Even if Southern congressmen would be successful in passing such laws, it wasn't going to have any effect around here. The leaders of Southern states quickly got a related message, and their own translation of it was, "We have got to declare our independence from this system of government that won't enforce its own laws". If juries can nullify, then states can nullify, and the national union was coming to an end. Both sides disagreed so strongly on this one issue they were willing, for the second time, to risk war for it.
Ku Klux Klan
The idea should be resisted that Jury Nullification is always a good thing. After the Civil War, many of the activities of the Ku Klux Klan were tolerated by sympathetic juries. Many lynch mobs of the Wild, Wild West were encouraged in the name of law and order. Prohibition of alcohol by the Volstead Act was imposed on one part of society by another, and Jury Nullification effectively endorsed rum-running, racketeering, and organized crime. The use of marijuana and abortion are two further examples where disagreement is so strong that compromise eludes us. What is at stake here is protecting the rights of a minority, within a society run by a majority. If minority belief is strong enough, jury nullification issues an unmistakable proclamation: "To proceed farther, means War."
 |
| Oliver Wendell Holmes |
That's a somewhat strange outcome for a process started by pacifist Quakers, so the search goes on for a better idea. Distinguished jurists differ on whether to leave things as they are. In a famous exchange, Oliver Wendell Holmes once had dinner with Judge Learned Hand, who on parting extended a lawyer jocularity, "Do justice, Sir, do justice." To which, Holmes then made the somewhat surly response, "That is not my job. My job is to apply the law."
Thus lacking any better approach, it is hard to blame the US Supreme Court for deciding this was something best left unmentioned any more than absolutely necessary. The signal which Justice Harlan gave in the majority opinion on the 1895 Sparf case was the very narrow ruling that a case may not be appealed, solely on the basis that the trial jury was not informed of its right to nullify the law in question. Encouraged by this vague hint, what has evolved has been a growing requirement that incoming jurors take an oath "to uphold the law", officers of the court (ie lawyers)are discouraged from informing a jury of its true power to nullify laws, and Judges are required to inform the jury in their charge that they are to "take the law as the judge lays it down" (ie leave appeals to higher courts). If a jury feels so strongly that it then persists in spite of those restraints, well, you apparently can't stop them. Nobody thinks this is a perfect solution, and aggrieved defendants like the Vietnam War protesters are quite vocal in their belief that the U.S. Supreme Court finally emerged with a visibly asinine principle: a jury does indeed have the right to nullify, but only as long as that jury is unaware it has that right. That's almost an open invitation to perjury if accurate; but while it's not precisely accurate, it comes close to being substantially true.
That's where matters stand, and apparently will stand, until someone finds better arguments than those of Benjamin Franklin, John Jay, Andrew Hamilton -- and William Penn.
Jersey
|
| Map of New Jersey |
Once you notice the oddity of salt water in the lower reaches of the Delaware and Hudson rivers, it gets easier to understand the current theory that southern New Jersey was once an island. Like Long Island, it was separated from the mainland by a sound, but in the Jersey case the sound silted up from Trenton to New Brunswick, creating a new peninsula of "West" Jersey by uniting the island with the mainland. The colony was named after the island of Jersey off the coast of England, a gesture for Sir George Carteret, who was given the American area out of gratitude for once sheltering the exiled royal brothers Charles II and James from Cromwell, in that other Jersey. Cape May was probably a second distinct island later joined to the larger one by the transformation of the silted ocean into the bogs of the Maurice River. Cape May started as a whaling community, populated by Quakers from New York and New England, who always maintained a social distance from the Philadelphia Yearly Meeting. The long Atlantic beaches of New Jersey now repeat the main geological process, with successive generations of barrier islands first heaved up by the ocean and then packed against the mainland, filling up the brackish bay. The cycle of forming and packing successive barrier islands takes about three hundred years before a new one starts. In a larger sense, the process consists of the former mountains of Pennsylvania crumbling into the ocean and then responding to wave action.
It's no mystery, therefore, why southern New Jersey is flat, broken up by turgid meandering streams which casually empty in either direction. The head of Timber Creek, which flows into Delaware, is only eight miles from the head of the Mullica River, flowing toward the ocean. During the Revolutionary War, the British found it too dangerous to sail up these winding creeks, since at any moment they might make a sharp turn and be facing a battery of cannon on the shore. An arrangement quickly grew up that buccaneers would build ships in the center of heavy oak forests and sail them out to Barnegat Bay, thence out one of the inlets of the barrier islands into the blue water. The financiers of Philadelphia, many of them with names now in the Social Register, would come from the rear, sailing up the Delaware River creeks, and walking the last mile or two to privateer headquarters on the Atlantic-flowing creeks. Auctions were conducted, in which the ships were examined, the captain interviewed, and the crew observed in target practice. If you bought a small share you would be rich when the ship returned; and if it never returned, well, you had to invest in a different one. New Jersey is indignant of the opinion that these privateers were mainly responsible for winning the Revolution, but given little credit for it. Many more British sailors were lost to the privateers than soldiers were lost to Washington's troops and the economic loss to Great Britain of the ships and cargoes eventually became serious. Since much of the profit from privateering was recycled into the American war effort by Robert Morris, the British found themselves facing an enemy much more formidable than just the ragged frozen troops at Valley Forge on the Schuylkill. Meanwhile, William Bingham was conducting a similar privateering operation in partnership with Morris but based on the island of Martinique, but that's another story.
In later centuries, the traditions and geography of the Jersey Pine Barrens suited themselves to smuggling and bootlegging during the era of alcohol Prohibition, and even after Repeal, high taxes on liquor kept bootlegging profitable. As late as the 1950s, there were divisions of FBI men prowling the woods of South Jersey, on the lookout for trucks carrying bags of cane sugar, or coils of copper tubing. After housing developments started to invade the forests, the hardball politics of South Jersey reflected a Mafia culture thought more characteristic of South Philadelphia. Near Vineland and Atlantic City, it isn't just a culture, it has the accent, because it also has some of the ancestry.
REFERENCES
| New Jersey, A Historical Account of Place names in the United States: Richard P. McCormick: ISBN-13: 978-0813506623 | Amazon |
Forming the State of Delaware

|
| Philip Yorke, Earl of Hardwicke |
When the Duke of York was within hours of being banished, he told his agent Sir John Werden to give the contested strip (now the state of Delaware) to Penn, but save out the town of Newcastle with a twelve-mile strip of land around it. Werden wrote that into the charter with a proviso based on the idea that the fortieth parallel was to the south of Newcastle, when in fact it was fifty miles north of it, and could not possibly conform to the stated boundaries. Both Penn and Baltimore learned the true situation in a year or two, and both attacked the other for dissembling ignorance, each seeking to take advantage of implausible arguments. What in fact they both discovered was that if the dividing line could be pushed a few miles south, Penn would acquire the mouth of the Susquehanna in the Chesapeake Bay, while if it went north a few miles, Maryland would acquire most of Philadelphia. Lord Hardwicke worked out a reasonable compromise which, while ignoring some plain language in the documents, eventually resulted in the Mason-Dixon line which is now reasonably comfortable for everybody, although first subjected to another two decades of wrangle.
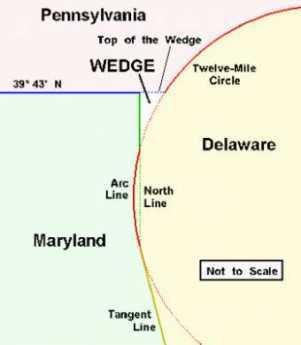
|
| Delaware Wedge |
Even part of the eventual compromise, a semicircular northern border, didn't come out right, resulting in a wedge of no-man's land. Landowners didn't enjoy paying disputed taxes, so they held up the settlement of the wrangle into the Twentieth Century. Eventually, the U.S. Supreme Court cut the wedge into two pieces, giving one piece each to Pennsylvania and Delaware. Meanwhile, disputes continued which had their basis in the way the semi-circular line was plotted out on the land. The surveyors ran 120 straight-line radii outward from the courthouse tower in Newcastle, and then connected the ends. Obviously, that resulted in 120 straight chords instead of a smooth semi-circle, and a couple of bulges had to be accommodated where the circle grazed other straight borders. The semi-circle crossed the Delaware River, so New Jersey helpfully abandoned its portion, only to regret its decision later when toll bridges were constructed, and ship channels deepened.

|
| King Charles I |
Two major societal changes took place between 1632 -- when Charles I granted the proprietorship of Maryland to the first Lord Baltimore -- and 1776 when all American real estate changed its rules. The first change was that the Delaware Bay morphed from a swamp into settlements of people; settlers came into possession. The second evolution was to the current view that if you sell some real estate it is no longer yours; in earlier eras, everything belonged to the king, who could take it away and give it to others as often as he pleased. In legal terms, the last king had the last word. Although acres of parchment were scribbled by lawyers pro and con, these considerations are what make clear how Lord Baltimore could hold the unchallenged legal title for fifty years to everything up to the fortieth parallel, but then have a court take away thousands of square miles. A land which was to become the three lower counties of Pennsylvania was given to William Penn by the Duke of York in 1682, using some flawed documents and only fully enjoyed by Penn's heirs for six years until they morphed into the new State of Delaware. From 1684 to 1769, legal ownership was a matter of continuing dispute. The exasperated Lord Chancellor (Hardwicke) in 1750 declared the case as one "of nature worthy of the judicature of a Roman senate rather than of a single judge".

|
| Lord Baltimore |
Lord Baltimore had been given "unsettled" land, occupied only by savages. William Penn's lawyers struggled to prove the Dutch had settled the area before 1632, while Baltimore's lawyers sought to prove that pirates and wandering fur traders don't count, nor do villages of thirty people who were wiped out by the Indians. By the Doctrine of Discovery, taking land from pagans was encouraged, but taking land from Christians required special formalities. Since this Doctrine dates back before there were Protestants, it might have been pertinent to inquire whether the Dutch should be regarded as pagans, as the Spanish surely did when they suppressed Dutch independence in the Eighty Years War, ending in 1648.
Lord Baltimore advertised land along Delaware for sale to settlers while the matter was still under litigation. That was the foulest play said Penn, a weak argument to make if litigation was intentionally pursued for a century.
Maryland favored the Catholic cause, so it seemed plausible for them to want to stall, hoping the Catholic Duke of York would ascend to the throne. Under the new King James II, however, Baltimore seemed unlikely to prevail that the same person, as Duke of York, really didn't own the land he was trying to give to William Penn. So of course, Lord Baltimore claimed he never stalled.

|
| Cape Henlopen |
And by the way, ocean currents moved Cape Henlopen a mile or so southward, but the real boundary problem was that common usage over the centuries confused Cape Henlopen with Fenwick's Island (to which it is usually attached by a thin barrier island), making an implicit difference in the Maryland/Delaware ownership of the corresponding strip of land at the southern border of the State of Delaware, a matter of a hundred or so square miles.
And all of this confusion was merely about the borders of one of the smallest of our fifty states. The political manner in which Delaware became a colony without a charter to the King, and became a state by gradual and mystifying degrees separate from the other counties of Pennsylvania are other complicated stories. Never mind the reasons Delaware remained in the Union during the Civil War, even though it also remained a slave state.
With gratitude to the memory of Dudley Cammett Lunt 1896-1981, whose books are a most readable but scholarly analysis of this complicated history. In particular, The Bounds of Delaware and, for the Mason-Dixon Line, Taylor's Gut in the Delaware State are recommended. The courts rejected arguments that the land was essentially wilderness when Lord Baltimore acquired his patent, and history has been sympathetic to Penn, the winner. The contention was the Dutch owned the land by right of discovery ( a Doctrine applied to land ruled by pagans by Pope Nicholas II in 1454), while the Duke of York later took it from the Dutch by surrender to force of arms -- another legally benign method of acquiring sovereignty. However, Lunt points out that a far more significant issue was the southern border of Pennsylvania in Penn's original grant, which asserted geographical impossibility to replace Maryland's plain and simply defined boundary. History has tended to regard this as understandable error, and subsequent legal quarrels to have been perpetuated by William Penn's greedy heirs. However, Lunt seems to reveal his own opinion of the affair by ending his book with a July 31, 1683 quotation from a letter by William Penn to Colonel Thomas Tailleur:
I, finding this place necessary to my Province and it ye Presence of Ld. Balt. was at Law, civil & common, I endeavoured to get it, & have it, & will keep it if I can.
Concessions and Agreements

|
| Concessions and Agreements |
The United States Constitution is a unique achievement, but it had significant precursors, many of which James Madison had studied at Princeton. In the days of difficult ocean travel, almost all colonies were bound by an agreement to maintain loyalty to their European owners in spite of receiving latitude to govern themselves. Charters and documents defining these roles were generally written by the owners, and the colonists could pretty much take them or leave them. In the case of New Jersey in 1664, however, a very formidable lawyer and friend of the King named William Penn was drawing up agreements to his own conditions of sale, taking care that the grant of governing authority he received was favorable. Penn's relationship to the King was unusually good, to say the least. He had more reason to be wary of nit-pickers in the King's administration, trying to anticipate every conceivable disappointment for some successor King.
For his part, Penn wanted to make colonial land attractive to re-sell to religious groups who had experienced harsh government oppression; he wanted no obstacles to his announcing there would be no religious oppression in New Jersey. He was offered the role of sub-king although he hastily rejected any such title, and needed to repeat the formalities of the Charter to define his role and reassure his settlers about that matter. Furthermore, he was dealing with the heirs of Carteret and Berkeley, active participants in North and South Carolina. So Penn's method of achieving basic rights was influenced by prior thinking in the Carolinas, as the thinking of John Locke secondarily influenced matters in Delaware and Pennsylvania. These ideas were incorporated in a New Jersey document called "Concessions and Agreements." The concepts were not wholly the ideas of William Penn, but he did write it, and it does contain many ideas that were uniquely his. Understandings about limits were set down, argued about, and agreed to. The owner risked money, the colonist risked his life. Neither would agree unless a reasonable bargain was struck in advance of any dispute. Furthermore, the main value of a colony was beginning to shift from trading rights to real estate rights. Carteret and Berkeley had not only been principals in both the Carolinas and the Jerseys but had been involved in a number of such investments in Africa and the West Indies; New Jersey was just another business deal. It was conventional for documents of this type to define the method of selection of a governor, the establishment of an assembly of colonists, and some sort of council to attend to day to day affairs. In that era, few colonists would cross the ocean without a guarantee of religious freedom, at least for their own brand of religion. Standard clauses which may sound strange in today's real estate world, were then necessary because it was a transfer of not merely land, but also the terms of government. In the case of the Quaker colonies, many of these stipulations were included in the earlier charter from the King. It seems very likely that Penn hovered around and negotiated these points which he wished to have the King agree to; and then once the land was safely his, Penn repeated and expanded these stipulations with the colonists in his Concessions and Agreements . It wasn't exactly a Constitution, but it reads a lot like the one America adopted a century later.

|
| Proprietors House |
Quakers had suffered persecution and imprisonment, and knew exactly what they feared; on the other side, it seems likely Carteret and Berkeley were less interested. So this real estate transfer document conceded almost anything the colonists wanted and the King would stand for, couched in conciliatory phrases. For example, no settler was to be molested for his conscience, and liberty was to be for all time, and for all men and Christians. Elections, by the way, must be annual, and by secret ballot. While law and order must prevail, nevertheless no man is to be imprisoned or molested except by the agreement of twelve men of the neighborhood. On the matter of slavery, no man was to be brought to the colony in bondage, save by his own consent (that is, indentured servants were to be permitted). And in what proved to be a final irony for William Penn, there was to be no imprisonment for debt. Almost all of these innovative ideas survived into the U.S. Constitution a century later, but the most innovative idea of all was to set them all down in a freely-made agreement in writing. This was not merely how a government was organized, it defined the set of conditions under which both sides agreed it would operate.
It was, of course, more than that. It was a set of reassurances to settlers who had been in New Jersey before the English arrived that they, also, would be treated as equals. It was a real estate advertisement to the fearful religious dissenters back in England that it was safe to live here. And it was a reminder to future Kings and Parliaments that this is what they had promised.
The pity and a warning, is that the larger vision of a whole continent governed fairly by common consent may have been too grandiose for a little band of New Jersey Quakers, surrounded as they were by an uncomprehending world. All utopias are helpless when stronger neighbors reject the basic premise. However, it was the expansion of the pacifist concept to the much larger neighboring territory of Pennsylvania that proved to be just too much for such a small group of friends to manage by consensus, particularly when unbelieving immigrants began to outnumber them. But the essential parts of it certainly remained in the minds of delegates to the Constitutional Convention in 1787. When the minutes of the Constitutional Convention speak of the "New Jersey Plan", the Concessions and Agreements was what they had in mind.
REFERENCES
| Concessions and Agreements of New Jersey 1676: William Penn | New Jersey State Library |
| Camden After the Fall: Decline and Renewal in a Post-Industrial City: Howard Gillette Jr.: ISBN-13: 978-0812219685 | Amazon |
13 Blogs
Unalienable Rights Before 1776
 Lawyers commonly say the Declaration of Independence "informs" the Constitution. But prior informing was performed by William Penn, the Roman Empire, and Hammurabi.
Lawyers commonly say the Declaration of Independence "informs" the Constitution. But prior informing was performed by William Penn, the Roman Empire, and Hammurabi.
A Brief WILLIAM PENN CHRONOLOGY, 1644-1718
 .
.
William Penn, Justice Holmes, and the Inner Light
 The hippies of the 1960s can be understood as just one extreme swing of an old, old pendulum.
The hippies of the 1960s can be understood as just one extreme swing of an old, old pendulum.
First Amendment: Separation of Church and State
 Eleven of the original thirteen colonies had,"established" religions. The separation of church and state by the First Amendment was not a statement of fact, but a worrisome departure from the past, mostly prompted by the behavior of the Virginia Episcopalians. For the Pennsylvania Quakers, disestablishment was a most disheartening event.
Eleven of the original thirteen colonies had,"established" religions. The separation of church and state by the First Amendment was not a statement of fact, but a worrisome departure from the past, mostly prompted by the behavior of the Virginia Episcopalians. For the Pennsylvania Quakers, disestablishment was a most disheartening event.
John Dickinson, Quaker Hamlet
 John Dickinson was the most respected lawyer and politician of his time. He had a lot to do with writing the Declaration of Independence but refused to sign it.
John Dickinson was the most respected lawyer and politician of his time. He had a lot to do with writing the Declaration of Independence but refused to sign it.
A Pennsylvania Farmer in Delaware
 John Dickinson achieved national fame in 1773 by publishing twelve letters written earlier denouncing the Townshend Acts. They were published anonymously as Letters From a Pennsylvania Farmer. His farm, curiously, was in Delaware.
John Dickinson achieved national fame in 1773 by publishing twelve letters written earlier denouncing the Townshend Acts. They were published anonymously as Letters From a Pennsylvania Farmer. His farm, curiously, was in Delaware.
The Origin of States Rights, a Rumination
The clamor for States Rights probably began with Virginia's claims for western territories.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Being a Small Country
 Remaining a small country has many merits, but one big demerit. Your neighbors are tempted to swallow you up.
Remaining a small country has many merits, but one big demerit. Your neighbors are tempted to swallow you up.
The Proprietorships of William Penn
 William Penn owned Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware; as the proprietor, he was the largest private American landowner, ever. Although the Revolutionary War mostly ended that, one of his proprietorships still owns all unclaimed land in southern New Jersey.
William Penn owned Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware; as the proprietor, he was the largest private American landowner, ever. Although the Revolutionary War mostly ended that, one of his proprietorships still owns all unclaimed land in southern New Jersey.
Jury Nullification
 William Penn demonstrated one of the most incisive legal minds in England by trapping the British courts in what remains a central unresolved dilemma for the law. He was the defendant in his own case. By the South's way of looking at things, it was a pacifist effort to restrain mindless abolitionism. Meanwhile, both sides calculated it would win if the South decided to fight.
William Penn demonstrated one of the most incisive legal minds in England by trapping the British courts in what remains a central unresolved dilemma for the law. He was the defendant in his own case. By the South's way of looking at things, it was a pacifist effort to restrain mindless abolitionism. Meanwhile, both sides calculated it would win if the South decided to fight.
Jersey
 Understanding New Jersey means understanding its unusual geography, and its Quaker origin as one of the three colonies owned by William Penn.
Understanding New Jersey means understanding its unusual geography, and its Quaker origin as one of the three colonies owned by William Penn.
Forming the State of Delaware
 In 1632, King Charles I granted to the Maryland proprietor coastal land with a northern border at the 40th parallel. In 1682, his son James the Duke of York evicted the Dutch from the Connecticut River to Cape Henlopen; afterward, his brother King Charles II gave away New Jersey and Pennsylvania, leaving York with New York plus a strip of wilderness from Pennsylvania to Henlopen. York then gifted that southern strip to William Penn before anyone realized there was a sloppy overlap with Maryland of thousands of square miles. Lawsuits are galore.
In 1632, King Charles I granted to the Maryland proprietor coastal land with a northern border at the 40th parallel. In 1682, his son James the Duke of York evicted the Dutch from the Connecticut River to Cape Henlopen; afterward, his brother King Charles II gave away New Jersey and Pennsylvania, leaving York with New York plus a strip of wilderness from Pennsylvania to Henlopen. York then gifted that southern strip to William Penn before anyone realized there was a sloppy overlap with Maryland of thousands of square miles. Lawsuits are galore.
Concessions and Agreements
 Most 17th Century colonies were proprietorships, requiring agreements for local autonomy without losing allegiance to the home country. William Penn cleverly expanded the New Jersey document into the intellectual precursor of the U.S. Constitution.
Most 17th Century colonies were proprietorships, requiring agreements for local autonomy without losing allegiance to the home country. William Penn cleverly expanded the New Jersey document into the intellectual precursor of the U.S. Constitution.